现实生活中,总会存在数据之间存在着某种关系,比如:用户 <-> 文章,用户 <-> 评论等。Elasticsearch 作为搜索引擎,在创建 Indices 时,是使用 Schema less 的数据结构。如果要在其实现不同数据的关系,官方提出了以下几种方式:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/current/application-joins.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/current/denormalization.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/current/nested-objects.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/guide/current/parent-child.html
如果对以上方式不清楚,直接点击上面的链接即可,这里就不再一一说明了,这里主要是对:Application-side joins、Nested objects、Parent/child relationships 三种方式进行对比,包括:索引性能和查询性能的对比。
- 测试环境
- 测试的模型
用户 <-> 对话:一个用户有多个对话,一个对话只能属于某个用户,用户和对话是一对多的关系。
1.Application-side joins
对话通过用户的 id,进行关联,mapping 如下:
1 | { |
2.Nested objects
把对话信息,作为 nested 字段内容,嵌入到用户数据中,mapping 如下:
1 | { |
3.Parent/child relationships
使用 Elasticsearch 自带的关系模型实现,mapping 如下:
1 | { |
- 测试结果
1.索引性能
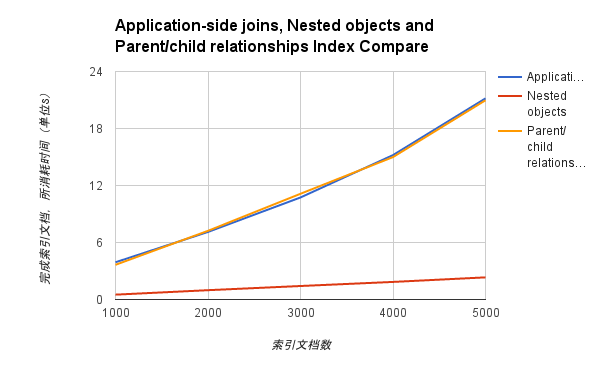
2.查询性能
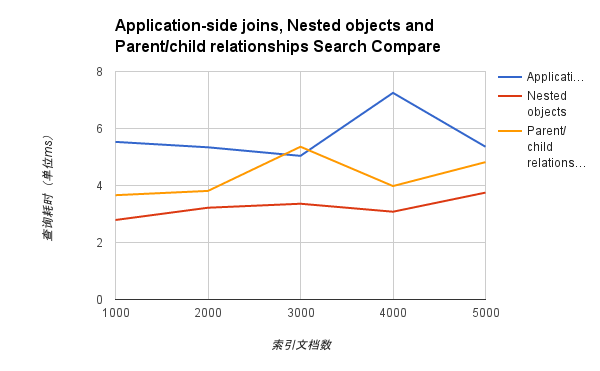
- 总结
从性能上 Nested objects 的性能都完胜 Application-side joins 和 Parent/child relationships。nested 的缺点是,查询出来的数据是整个 document,所以还需要在应用程序中做额外的过滤操作。