Celery Route 模块解读。
最近在线上观察时发现了有任务的队列堆积了,当时判断是同事写的 Celery crontab 任务堆积了,当时他给我看了线上的配置,他说没有指定定时任务的队列,会造成堆积,但是这个配置在线上已经运行了好几个月了,如果原因是这个,那很早之前就暴露问题了,不过本人对 Celery 还停留在会使用的阶段,一些内部细节不是很了解,所以在周末抽了时间来一探究竟。
在对源码进行 grep 和 rdb(celery 的远程调试后),确定了能够解决的疑惑的位置在 Celery route 模块。
这里结合下面一段示例代码,对 Celery route 进行解读(使用 Celery 版本为 3.1.21)。
1 | # -*- coding: utf8 -*- |
PS: 这里示例代码虽然是演示 Periodic,但是对于普通 Task 也一样。
运行后截图:
- Celery beat
- Celery Periodic Task
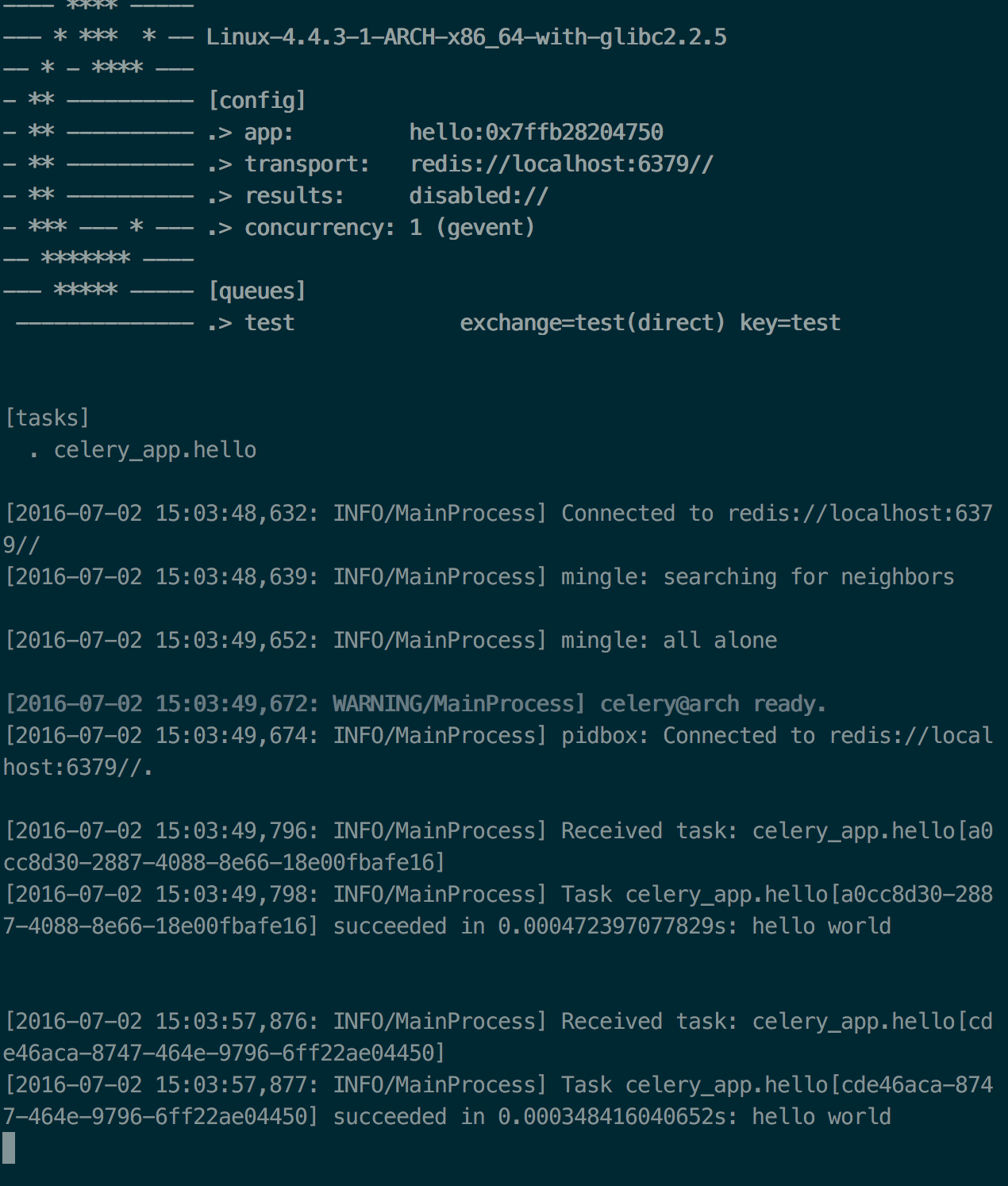
可以看到控制台中,task 会每隔 30s 运行一次,并返回 hello world。
那接下来,我们就开始讲解 Celery Route 吧。
在上面的代码中,有一段这样的配置代码:
1 | app.conf.CELERY_ROUTES = { |
上面的代码的意思是,在 celery_app 这个 Celery application 下,名为 hello 的任务,只消耗来自于队列 test 的任务。
Celery Beat
这里把 Celery Beat 的调用链抽象出来,大致的流程如下:
1 | tick -> send scheduler -> send to task |
这里主要关注 send to task 这步,而这步主要使用 Celery 对象中定义的 send_task 方法。
1 | def send_task(self, name, args=None, kwargs=None, countdown=None, |
上面和 route 相关的代码有:
- 获取 route: router = router or amqp.router
- 获取 route options: options = router.route(options, route_name or name, args, kwargs)
Router
一般情况下,这里的 router 就是 amqp.router。而 amqp.router,则是 celery.app.routes.Router 的实例化对象。接下来我们看创建该实例化对象都做了什么,代码如下:
1 | def Router(self, queues=None, create_missing=None): |
这里有四个初始化参数,主要着重以下 3 个:
- self.routes
其是一个描述符,里面存储的是路由表信息,这些路由表的信息使用以下代码获取:
1 | def flush_routes(self): |
其中 _routes 是 celery.app.routes 模块,而路由表的信息,则有 CELERY_ROUTES 提供,其中 prepare 方法定义如下:
1 | def prepare(routes): |
这里主要是预先生成好,route 表的类型,由 MapRoute (包括了 Dict,且是默认路由类型),其它都是自定义的路由类型,上面的例子所使用的便是 MapRoute 类型的路由表。
- queues or self.queues
这里 queues 没有特别指明,都是默认的 celery.amqp.Queues 的实例化对象,其中 Queues 继承于 dict:
1 | @cached_property |
在没有指定 CELERY_QUEUES 时,默认会创建一个名为 celery 默认队列:
1 | if not queues and conf.CELERY_DEFAULT_QUEUE: |
- create_missing
这个属性很重要,特别是在生产环境中,当 Celery 发现 task 需要的队列不存在会自行创建相应的队列。
1 | def __missing__(self, name): |
由于 Queues 是继承于 dict,这里 override 了 magic method __missing__,这样就可以在 self.create_missing 开启时,自行创建不存在的队列。
Router Options
1 | options = router.route(options, route_name or name, args, kwargs) |
options 是通过 router.route 进行获取的,其详细代码如下:
1 | def route(self, options, task, args=(), kwargs={}): |
这里先讲解以上代码的含义,对 lookup_route 和 expand_destination 放在后面。上面的含义是首先从 expand_destination 中获取扩展的选项。接着检查是否由路由信息,如果有,则查找该路由信息是否含有 task 对应的路由信息,如果有,则将对得到的路由信息 route 扩展之后,与 options 合并之后返回;如果 routes 不存在,并且 options 没有队列的信息,则使用默认的队列 celery,并与原 options 合并之后返回。
其中使用到的 lookup_route 和 expand_destination 代码如下:
- lookup_route
1 | def lookup_route(self, task, args=None, kwargs=None): |
用于查询路由表信息,这里的 _first_route 方法定义如下:
1 | _first_route = firstmethod('route_for_task') |
而 firstmethod 的定义如下:
1 | def firstmethod(method): |
这两段代码的含义时,_first_route 使用 route 定义的方法 route_for_task 在 self.routes 路由表中是否存在 task 对应的路由信息,如果有则返回,否则返回 None。
- expand_destination
1 | def expand_destination(self, route): |
该方法的主要作用是检查 self.queues 是否存在 queue 对应的队列:
1 | self.queues[queue] |
如果 create_missing = True 这里会创建 missing 的队列,返回的 Q 是 kombu.Queue 的实例化对象。
如果 task 指定了队列 queue,这里会修改路由表里面的 queue 会 Q 后返回。
以上便是 Celery 中 Route 的解读。通过对源码的解读,验证了当时自己的判断是正确的堆积的并不是因为 Periodic task 的配置没有写 queue 信息。
目前,我司线上的 Route 的配置就像我上面使用 dict configuration 方式进行的,而 celery 官方并不推荐,相反推荐的是这样的方式:
1 | # -*- coding: utf8 -*- |
这样做是利用到了 CELERY_CREATE_MISSING_QUEUES (默认为 True),自动创建不存在队列的,这样可以避免写太多冗余的配置的情况。